THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Climate change drives severe weather, rising sea levels, and ecosystem disruptions. Recognizing these effects is crucial for urgent action and adapting to our changing world.
"The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) reports significant reductions in Arctic sea ice extent and glacier mass worldwide."
Climate change is having profound effects on the planet, influencing various aspects of the natural world and human societies. The impacts are widespread, ranging from environmental changes to significant socio-economic consequences, all of which are supported by extensive scientific research.
One of the most evident elements of climate change is the rise In global temperatures. According to NASA, the Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. This warming trend has been linked to changes in weather patterns, resulting in more frequent and intense heat waves. Studies published in “Nature” have shown that these rising temperatures contribute to shifts in climate zones and can affect local ecosystems and biodiversity.
The consequences of these temperature increases are particularly noticeable in polar and glacial regions. The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) reports significant reductions in Arctic sea ice extent and glacier mass worldwide. These changes contribute to rising sea levels, which threaten coastal communities with increased flooding and erosion. The World Glacier Monitoring Service (WGMS) highlights that the accelerated melting of glaciers has far-reaching effects on freshwater supplies and sea level rise.
"Research from Science emphasizes that disruptions in temperature and precipitation patterns can threaten biodiversity and lead to the decline of various species."
In addition to temperature changes and melting ice, climate change is also affecting weather patterns and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), there has been a noticeable rise in the intensity and occurrence of severe weather events, including hurricanes, heavy rainfall, and droughts. These extreme weather events pose risks to infrastructure, agriculture and water resources and can lead to significant economic losses and humanitarian issues.
The effects of climate change extend to ecosystems as well. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns Impact species distributions, leading to altered migration patterns and changes in habitat. Research from “Science” emphasises that these disruptions can threaten biodiversity and lead to the decline of various species
Addressing these effects requires a comprehensive approach that includes both mitigation and adaptation strategies. Understanding the science behind these impacts and implementing effective policies can help manage the risks and work towards a more resilient and sustainable future.
THE FOLLOWINGS ARE THE FOUR MAIN EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
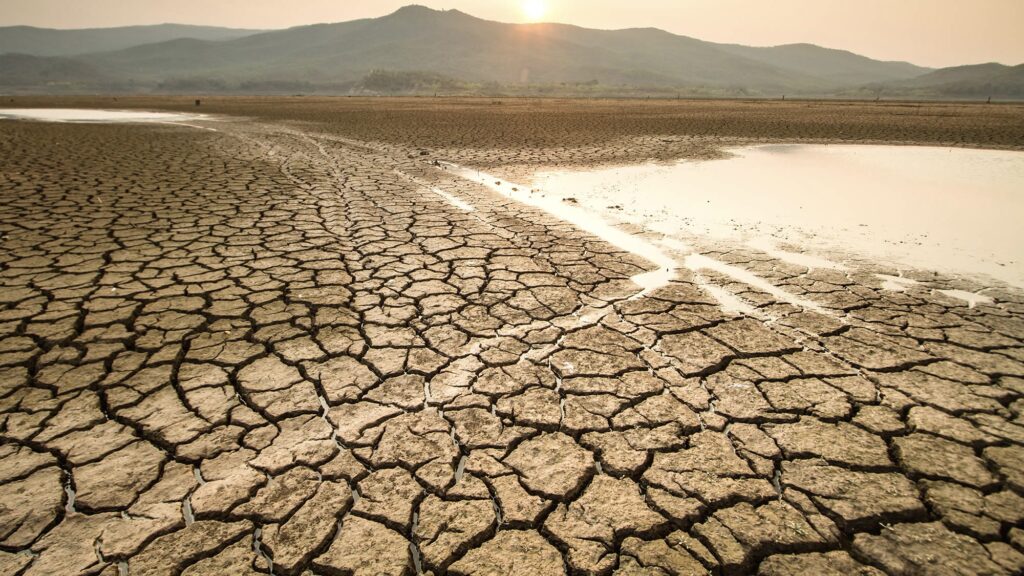
RISING SEA LEVELS
Melting polar ice and glaciers, combined with the thermal expansion of seawater due to higher temperatures, cause sea levels to rise. This increases the risk of coastal flooding, erosion, and habitat loss.
Image Credit: Creative Commons Attribution-SharelAlike 4.0

MORE EXTREME WEATHER EVENTS
Climate change amplifies weather extremes, resulting in more intense hurricanes, heat waves, droughts, and heavy rainfall. These changes lead to severe environmental impacts, infrastructure damage, and increased frequency of natural disasters.
Image Credit: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0
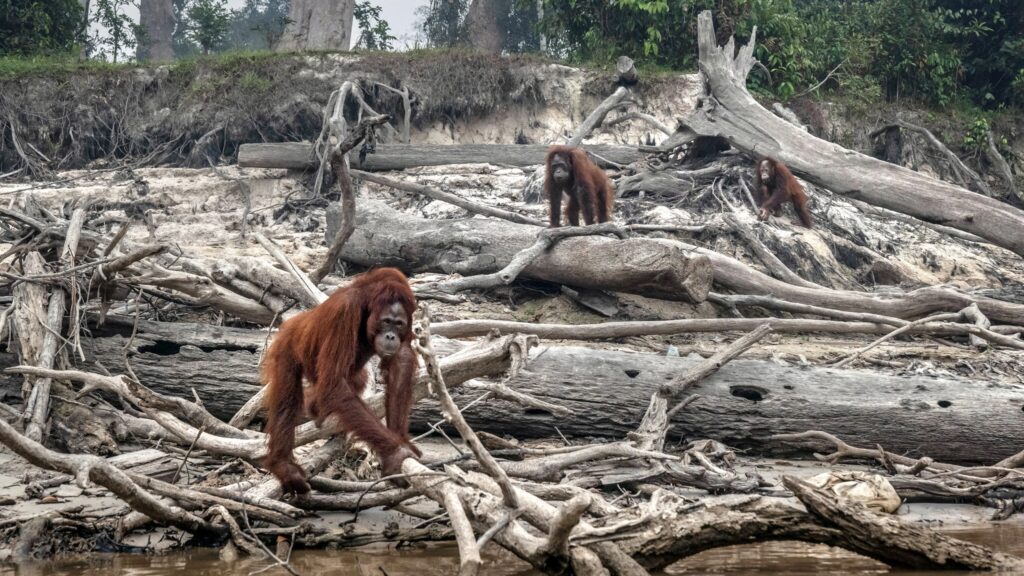
DISRUPTION OF ECOSYSTEM
Changes in temperature and precipitation disrupt natural habitats, causing shifts in species distributions and altering migration patterns. This can lead to reduced biodiversity and threaten the survival of various plant and animal species.
Image Credit: Creative Commons Attribution-SharelAlike 4.0
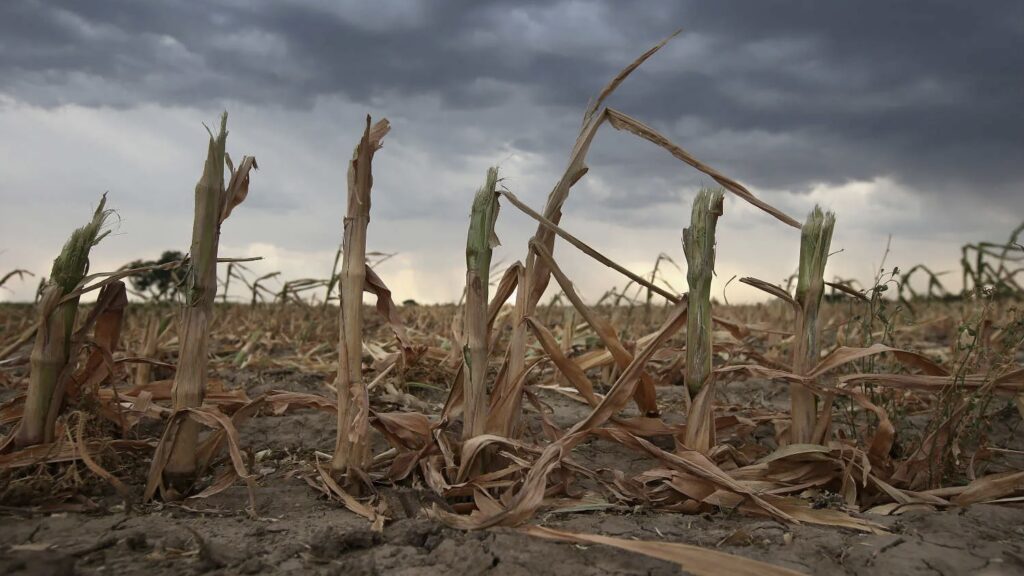


DECREASED AGRICULTURAL YIELDS
Climate change affects crop yields by altering growing seasons, increasing the frequency of pests and diseases, and impacting water resources. These changes pose significant challenges to food security and agricultural productivity worldwide.
Image Credit: Creative Commons Attribution-SharelAlike 4.0
References
1. National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), 2021. Arctic Sea Ice News & Analysis. Available at:
https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/
2. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2021. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press. Available at:
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
3. Science, 2019. Climate Change and Ecosystem Disruption. Science. Available at:
https://www.sciencemag.org/collections/climate-change
4. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 2020. The State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture. FAO. Available at:
https://www.fao.org/3/ca3130en/CA3130EN.pdf